
📌 매뉴얼 (Linux)
NAME
waitpid - wait for process to change state
: 프로세스가 상태를 변경할 때까지 기다리기
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *wstatus, int options);
DESCRIPTION
All of these system calls are used to wait for state changes in a child of the calling
process, and obtain information about the child whose state has changed. A state change is
considered to be: the child terminated; the child was stopped by a signal; or the child was
resumed by a signal. In the case of a terminated child, performing a wait allows the system
to release the resources associated with the child; if a wait is not performed, then the ter‐
minated child remains in a "zombie" state (see NOTES below).
If a child has already changed state, then these calls return immediately. Otherwise, they
block until either a child changes state or a signal handler interrupts the call (assuming
that system calls are not automatically restarted using the SA_RESTART flag of sigaction(2)).
In the remainder of this page, a child whose state has changed and which has not yet been
waited upon by one of these system calls is termed waitable.
wait() and waitpid()
The wait() system call suspends execution of the calling thread until one of its children ter‐
minates. The call wait(&wstatus) is equivalent to:
waitpid(-1, &wstatus, 0);
The waitpid() system call suspends execution of the calling thread until a child specified by
pid argument has changed state. By default, waitpid() waits only for terminated children, but
this behavior is modifiable via the options argument, as described below.
The value of pid can be:
< -1 meaning wait for any child process whose process group ID is equal to the absolute
value of pid.
-1 meaning wait for any child process.
0 meaning wait for any child process whose process group ID is equal to that of the call‐
ing process at the time of the call to waitpid().
> 0 meaning wait for the child whose process ID is equal to the value of pid.
: 이 모든 시스템 호출은 호출 과정의 자식에서 상태 변경을 대기하고 상태가 변경된 child에 대한
정보를 얻는 데 사용됩니다. 상태 변경은 다음과 같이 간주됩니다. child가 종료되거나,
신호에 의해 child가 중지되거나, 신호에 의해 다시 시작됩니다. 종료된 child의 경우,
대기를 수행하면 시스템이 child과 관련된 리소스를 해제할 수 있고, 대기를 수행하지 않으면
종료된 child는 "좀비" 상태로 유지됩니다(아래 참고 참조).
child가 이미 상태를 변경한 경우 이러한 호출은 즉시 반환됩니다.
그렇지 않으면 child이 상태를 변경하거나 신호 처리기가 호출을 중단할 때까지
(시그액션(2)의 SA_RESTART 플래그를 사용하여 시스템 호출이 자동으로
다시 시작되지 않는다고 가정할 때) 차단됩니다.
이 페이지의 나머지 부분에서는 상태가 변경되어 아직 이러한 시스템 호출 중 하나가
대기하지 않은 child를 대기 가능 상태라고 합니다.
wait() and waitpid()
wait() 시스템 호출은 하위 호출 중 하나가 종료될 때까지 호출 스레드의 실행을 중지합니다.
호출 wait(&wstatus)는 다음과 같습니다:
waitpid (- 1, &wstatus, 0);
waitpid() 시스템 호출은 pid 인수에 의해 지정된 child이 상태가 변경될 때까지 호출 스레드의 실행을 중지합니다.
기본적으로 waitpid()는 종료된 child만 대기하지만, 이 동작은 아래 설명된 대로 옵션 인수를 통해 수정할 수 있습니다.
pid 값은 다음과 같습니다:
< -1은 프로세스 그룹 ID가 pid의 절대값과 동일한 하위 프로세스를 대기한다는 것을 의미합니다.
-1은 모든 자식 프로세스를 기다릴 것을 의미합니다.
0은 호출 시 프로세스 그룹 ID가 호출 프로세스 ID와 동일한 하위 프로세스를 waitpid()로 기다리는 것을 의미합니다.
> 0은 프로세스 ID가 pid 값과 동일한 child를 기다린다는 뜻입니다.
RETURN VALUE
waitpid(): on success, returns the process ID of the child whose state has changed; if WNOHANG
was specified and one or more child(ren) specified by pid exist, but have not yet changed
state, then 0 is returned. On error, -1 is returned.
Each of these calls sets errno to an appropriate value in the case of an error.
: 성공 시 상태가 변경된 자식의 프로세스 ID를 반환합니다.
WNOHANG이 지정되었고 pid로 지정된 자식(자녀)이 하나 이상 존재하지만 상태가 아직 변경되지 않은 경우
0이 반환됩니다. 오류 시 -1이 반환됩니다. 이러한 각 호출은 오류가 발생할 경우 적절한 값으로 errno를 설정합니다.
📌 함수 설명
waitpid 함수는 wait 함수와 달리 원하는 pid의 child process를 기다릴 수 있는 함수이다.
pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options); 의 형태이고, 인자로 받는 pid에 따라 waitpid의 처리가 달라진다.
pid에 따라서 어떠한 프로세스를 기다릴지를 지정할 수 있는데, 다음과 같은 옵션으로 이뤄져있다.
< 인자 pid에 따른 옵션 >
| pid == -1 | 임의의 자식 프로세스 |
| pid > 0 | 프로세스 ID가 pid의 값과 같은 자식 프로세스 |
| pid == 0 | 프로세스 그룹 ID가 호출한 프로세스의 ID와 같은 프로세스 |
| pid < -1 | 프로세스 그룹 ID가 pid의 절대값과 같은 임의의 자식 프로세스 |
우선 프로세스 그룹이란, 관련있는 프로세스를 묶은 것으로 Process Group ID를 부여받는다.
프로세스는 그룹 멤버가 되며, 쉘에서 파이프로 연결하면서 프로세스 그룹으로 묶어 한 작업으로 처리할 수 있다.
또한, 프로세스 그룹 리더가 존재하며, 그룹 리더의 PID가 PGID(Process Group ID)가 된다. (리더 변경 가능)
위 표에 적힌 해당 프로세스가 wait할 대상이 되고, 각각 설명하면,
-1일 때는, wait() 함수와 동일하게 하나의 자식 프로세스가 종료할 때까지 기다린다. (waitpid(-1, &status, 0))
0 보다 클 때는, 해당 pid의 자식 프로세스가 종료할 때까지 기다린다.
0일 때는, 현재 프로세스의 그룹 ID와 같은 그룹의 자식 프로세스가 종료할 때까지 기다린다.
-1보다 작을 때는, 그룹 ID가 pid로 받은 값의 절댓값과 같고, 해당 그룹의 자식 프로세스가 종료할 때까지 기다린다.
그리고, 3번째 인자인 options에는 0, WNOHANG, WCONTINUED, WUNTRACED 등이 들어가며,
일반적으로 WNOHANG(자식 프로세스가 종료되었는지 실행중인지만 확인하고 기다리지는 않음.) 과
0 (일반 wait 함수처럼 자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 기다림.) 을 많이 사용한다.
반환값은 wait와 마찬가지로 종료된 자식 프로세스의 프로세스 ID를 return 하고 , 실패하면 -1을 반환한다.
추가적으로 'WNOHANG을 options으로 사용하면서 자식 프로세스가 종료되지 않았다면' 0을 반환한다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int pid = fork();
int status;
if (pid == 0)
{
sleep(5);
printf("Child Process Ended\n");
exit(0);
}
while(waitpid(pid, &status, WNOHANG) == 0)
{
sleep(1);
printf("waiting...\n");
}
printf("Parent Process Ended\n");
exit(0);
}
출력 - std_output)
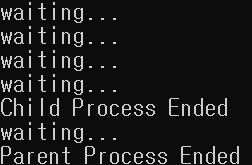
waitpid의 options을 WNOHANG으로 사용하고 while문에 0일 때의 조건을 주었는데,
'WNOHANG을 options으로 사용하면서 자식 프로세스가 종료되지 않았다면' 0을 반환하는 상황을 이용한 코드이다.
자식은 sleep을 5초간하고 이후에 Child Process Ended 라는 문구를 출력한다.
waitpid는 부모 프로세스가 그 자식이 종료될 때까지 기다리는 것이 아닌, 바로 0을 반환하게 되므로,
while문 안의 내용을 실행하여 1초 sleep 후, waiting... 을 출력한다.
그리고 자식이 종료되면, 이제 부모 프로세스는 waitpid가 0이 아닌 자식의 pid를 반환하므로 반복문이 종료되고,
Parent Process Ended가 출력되며 모두 종료된다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int pid = fork();
int status;
if (pid == 0)
{
sleep(5);
printf("Child Process Ended\n");
exit(0);
}
while(waitpid(pid, &status, 0) == 0)
{
sleep(1);
printf("waiting...\n");
}
printf("Parent Process Ended\n");
exit(0);
}
출력 - std_output)

첫번째 코드에서 waitpid의 options을 0으로 바꾼 뒤의 결과이다.
그럼 wait() 함수와 동일하게 작동하며, 자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 기다리다, 종료되면
해당 자식 프로세스의 pid를 반환하므로 반복문이 실행되지 않는다.
그리하여, Child, Parent의 프로세스 종료 출력만 되고 끝이 난다.
'프로그래밍 > C' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [library] strjoin 구현하기 (0) | 2024.06.26 |
|---|---|
| [library] substr 구현하기 (0) | 2024.06.18 |
| [function] wait 함수 알아보기 (0) | 2024.06.09 |
| [function] unlink 함수 알아보기 (2) | 2024.06.07 |
| [function] pipe 함수 알아보기 (0) | 2024.06.06 |



